CELL ORGANELLES
CELL ORGANELLES
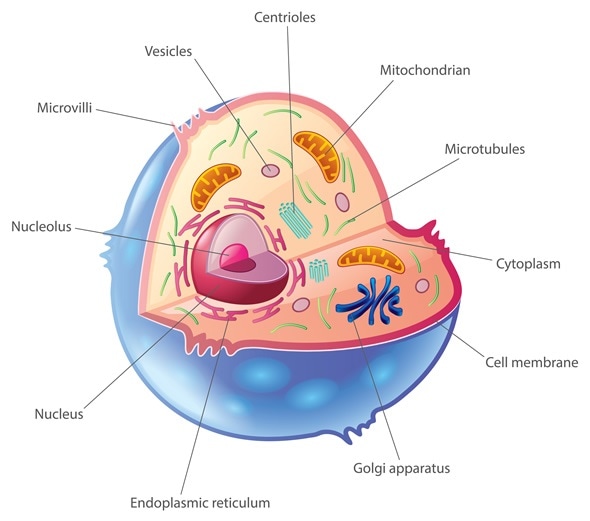

A small organ-like structure present inside the cell is called a cell organelle. It has a particular structural makeup and performs a specific function. Depending upon the presence or absence of membrane, cell organelles can be classified into three categories, namely:
- Without membrane: Some cell organelles like ribosomes are not bounded by any membrane. They are present in prokaryotic as well as eukaryotic organisms.
- Single membrane-bound: Some organelles are bounded by a single membrane. For example, vacuole, lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum etc. They are present only in a eukaryotic cell.
- Double membrane-bound: Cell organelles like mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles. They are present only in a eukaryotic cell.
https://www.toppr.com/guides/biology/the-fundamental-unit-of-life/cell-organelle/
Cell Organelle
|
Occurrence/ Characteristic & Structure
|
Function
|
Cell Membrane/ Plasma Membrane
|

|
|
Cell Wall
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
Nucleus
(Director/ Brain of the Cell)
|
 |
|
Mitochondria (The Power House of The Cell / Storage Batteries)
|
 | |
Golgi Bodies
(Shipping Department of Cell)
|
 |
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
(Framework of Cell)
|
 |
|
Vacuole
|
|
|
Lysosomes (Suicidal bags of Cell, natural scavenger, cellular housekeeper)
|
|
|
Ribosomes (Protein Factories)
|
 |
|
Plastids
|
Types-
 |
|


Comments
Post a Comment