ECOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS
ECOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS

Are you alone in this world? Of course not! You have many human beings surrounding you always! Similarly, if you see the population of other organisms, you will find many organisms living together. None of the organisms in this world can survive alone. This interaction between populations gives rise to population interaction. Let us learn further.
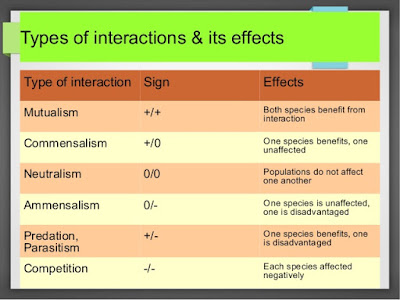
Mutualism
When the two different population species interact in such a manner that it is beneficial to each other, then this form of interaction is called mutualism. Lichens are a classic example of mutualism in between fungi and algae. Even plants and animals show good mutualism.
Plants need some agents for pollination and seed dispersal. And these agents are the animals. Animals, in turn, are rewarded with the nectar or the fruits of the plants. But, even in mutualism, there are some cheater species, which may not reward the other species. This leads to co-evolution of the species.
EXAMPLE : FLOWER AND BUTTERFLY.
Competition
When the closely related species fight for limited resources, there is a competition between the species. These types of interactions are called competition. This fight for resources can occur between diverse groups of the population also.
Competition can occur even when there is an unlimited supply of resources. Here, it depends on the superiority of one species over the other. In the presence of one population species, the other population species may not use the resources effectively. But if the dominant species is removed, then the other species will use the resources to their full capacity.
EXAMPLE : MANGO TREE AND VANDA
PREDATION
This interaction is a very important one as it ensures that there is stability in the ecosystem. The two main populations interacting in predation are the predators and the prey.
Without the predators, the prey population will go out of control. The species diversity in a community is also maintained by the predators. They reduce the intensity of the competition between prey species. The prey species have also evolved several mechanisms to lessen the impact of predation.

EXAMPLE : DEER AND TIGER
Parasitism
This is an interaction of populations where a parasitic mode of nutrition is clearly seen, with one species being completely dependent on the other host species for all its meals/ nutrient requirements. Parasitism is clearly seen in many taxonomic groups, right from plants to higher vertebrates.
EXAMPLE : MANGO TREE AND LORANTHUS
COMMENSALISM
In this kind of integration, one species population benefits from the other species population. But the other species population does not benefit nor is it harmed in any way. If you have been to rural areas, you have seen many birds perching on cattle.
Here the cattle do not benefit anything nor cause any harm. But as the cattle moves, they stir up the small insects hiding in the grass. It is these insects that the birds feed on, thereby benefiting to large extent.
EXAMPLE : MANGO TREE AND VANDA


Comments
Post a Comment