ECOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS
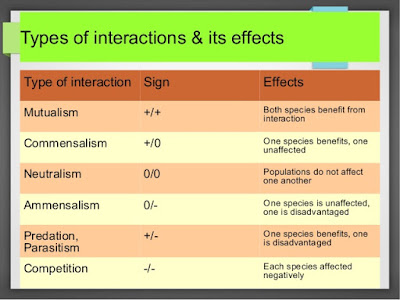
ECOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS Are you alone in this world? Of course not! You have many human beings surrounding you always! Similarly, if you see the population of other organisms, you will find many organisms living together. None of the organisms in this world can survive alone. This interaction between populations gives rise to population interaction. Let us learn further. Mutualism When the two different population species interact in such a manner that it is beneficial to each other, then this form of interaction is called mutualism . Lichens are a classic example of mutualism in between fungi and algae. Even plants and animals show good mutualism. Plants need some agents for pollination and seed dispersal. And these agents are the animals. Animals, in turn, are rewarded with the nectar or the fruits of the plants. But, even i...

